• Documentación instantánea del ángulo iridocorneal en fotografías en color real.
• Tiempo libre para que los médicos evalúen y planifiquen el tratamiento.
• Gonofotografía circunferencial automatizada.
• Funciones adicionales con GS Viewer para NAVIS-EX
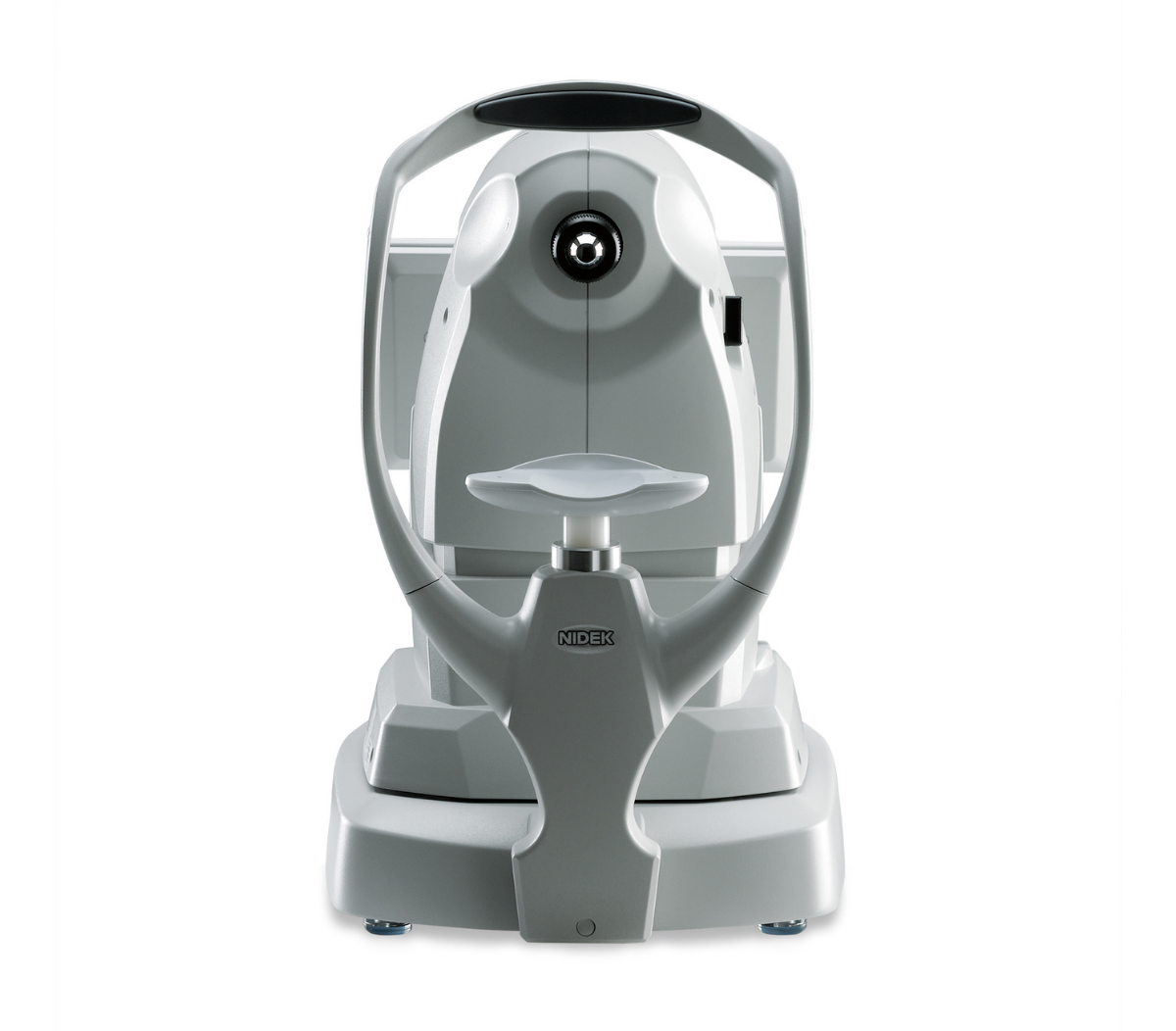
GS-1
¡El Revolucionário Gonioscopio!
¡Documente, Evalúe y Planifique!
Una imagen vale más que mil palabras!
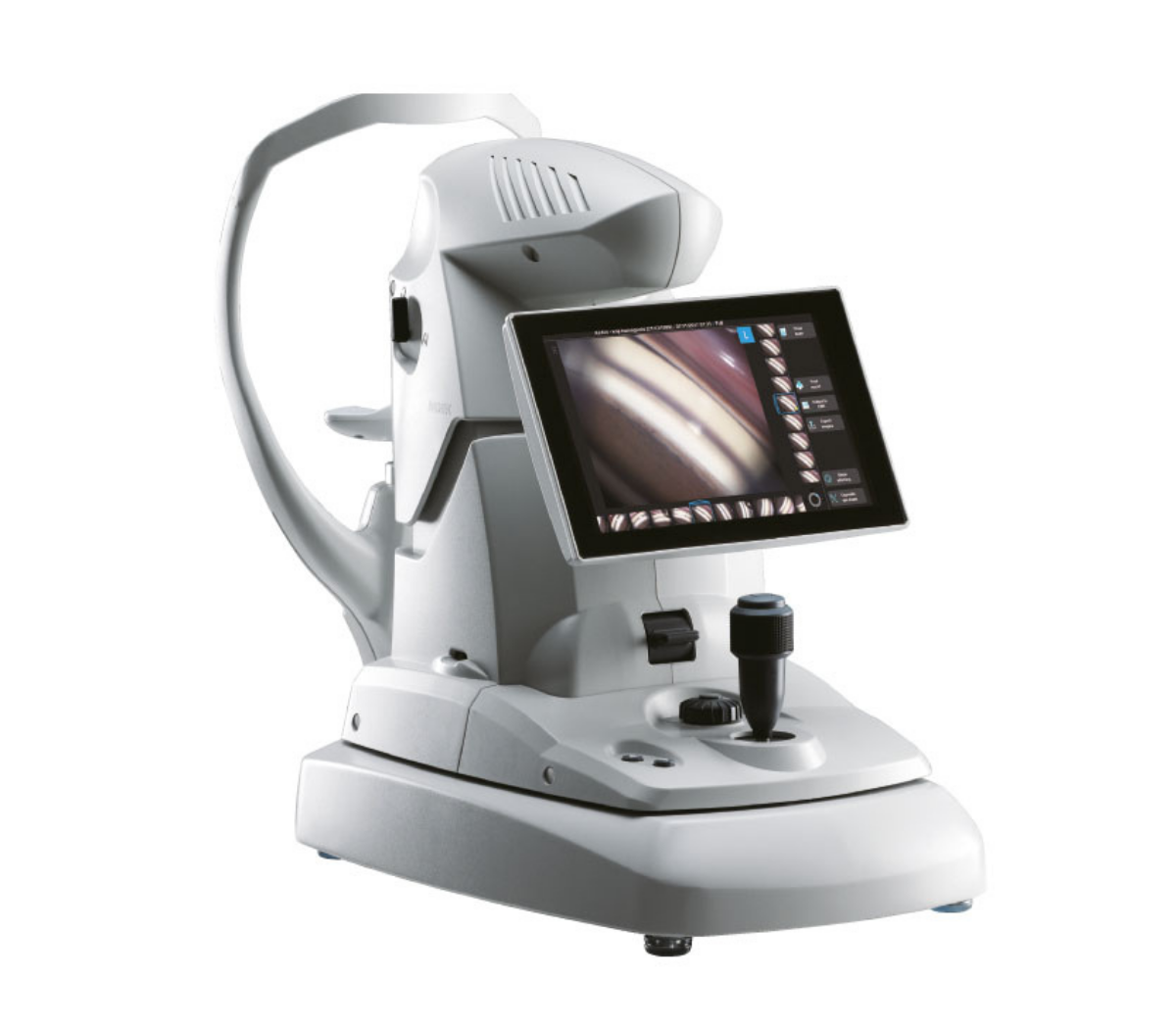
Documentación al instante con el GS-1
El GS-1 documenta al instante al ángulo iridocorneal en fotografías a color reales y las almacena en el dispositivo. Por lo tanto, no es necesario disponer de dibujos o bocetos detallados en la ficha del paciente para registrar la patología del ángulo.
Las fotografías del GS-1 pueden adjuntarse a la ficha o al archivo del paciente. Documnetar con el GS-1 es mucho más sencillo y definitivo que los bocetos subjetivos de la patologia.
-
- Goniofotografía circunferencial automatizada
- Medición por inmersión con gel de no-contacto
- Exportación de imágenes
¡Documente,
evalúe y
planifique!
Una imagen vale más que mil palabras
El GS-1 documenta instantáneamente el ángulo iridocorneal en fotografías en color real y las almacena en el dispositivo. Por lo tanto, no hay necesidad de dibujos o bocetos detallados en la historia clínica del paciente para registrar la patología angular. Las fotografías del GS-1 se pueden adjuntar al archivo o cuadro del paciente. La documentación con el GS-1 es mucho más simple y mucho más definitiva que los bocetos subjetivos de la patología.
Fácil documentación y evaluación con el GS-1.
Las fotografías pueden verificarse en la pantalla táctil del dispositivo y ampliarse fácilmente.
La evaluación de la estructura angular y la patología se facilita fácilmente mediante la revisión de fotografías digitales durante la evaluación clínica, en lugar de realizar una gonioscopia manual. Las fotografías digitales del GS-1 se pueden compartir de técnicos a clínicas, con colegas clínicos, médicos y pacientes remitentes, junto con la documentación completa de los resultados del GS-1.
Enfoque en la Evaluación y la Planificación
La delegación del funcionamiento del GS-1 permite a los profesionales médicos centrarse en la evaluación del paciente y la planificación del tratamiento.
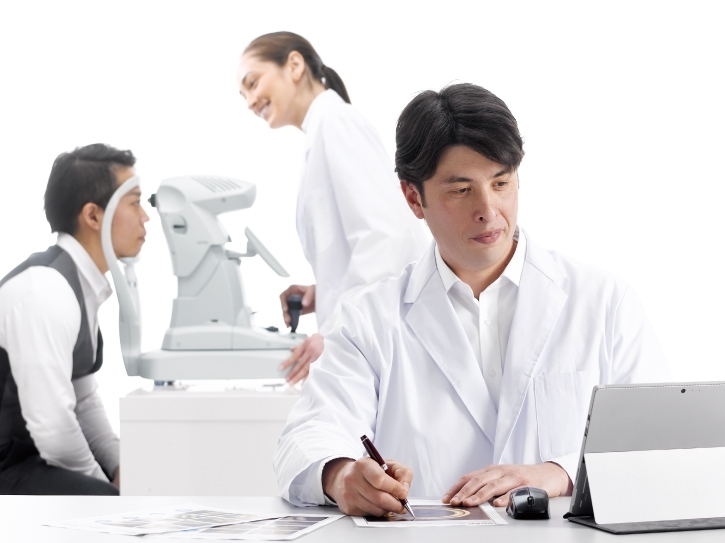

Consulta con Otros Compañeros Médicos
Las goniofotografías digitales facilitan la realización de consultas con otros compañeros médicos para mejorar la evaluación de los casos que tienen un
diagnóstico más difícil.

Transferencia Efectiva de la Información a las Clínicas Asociadas
Para aquellos pacientes que requieren de cuidados post-operatorios en otro lugar, las goniofotografías digitales pueden enviarse fácilmente a las clínicas de referencia.
Mayor Facilidad para Obtener el Consentimiento del Paciente
Las goniofotografías a color facilitan la educación del paciente y su consentimiento para los procedimientos quirúrgicos.

GS-1 ahorra tiempo a los médicos para evaluar y planificar el tratamiento. Las fotografías digitales de gonio agregan la conveniencia de reevaluar el ángulo completo en cualquier momento. Las fotografías en color de alta resolución mejoran la calidad de la evaluación y permiten un monitoreo integral.
Ejemplos Postoperatorios*:
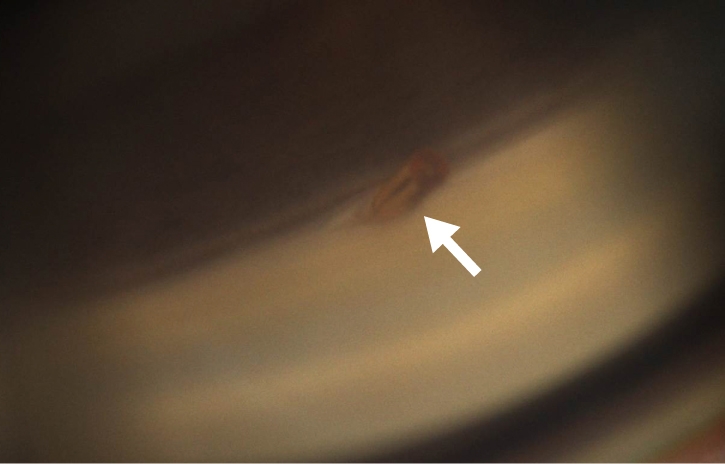
MIGS (Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery)
Diagnóstico pre-operatorio: POAG (Glaucoma Primario de Ángulo Abierto, por sus siglas en inglés)
MIGS (Cirugía de glaucoma mínimamente invasiva, por sus siglas en inglés) situada por encima del espolón escleral
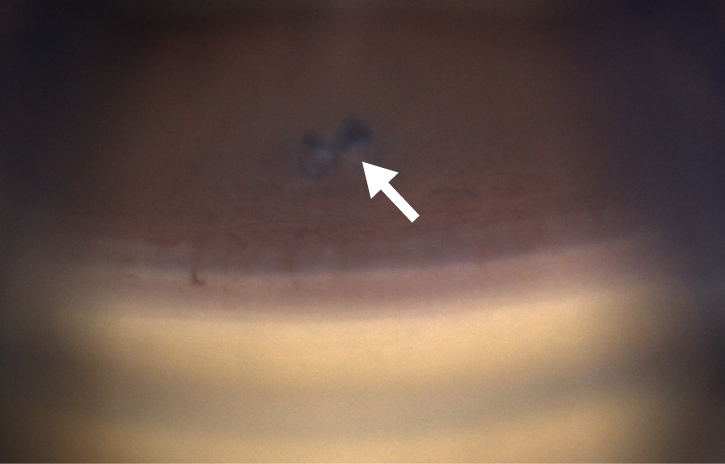
Iriditomía con láser
Diagnóstico pre-operatorio: PACG (Glaucoma Primario de Ángulo Cerrado, por sus siglas en inglés)
Iridotomía periférica visible que da como resultado un ángulo abierto
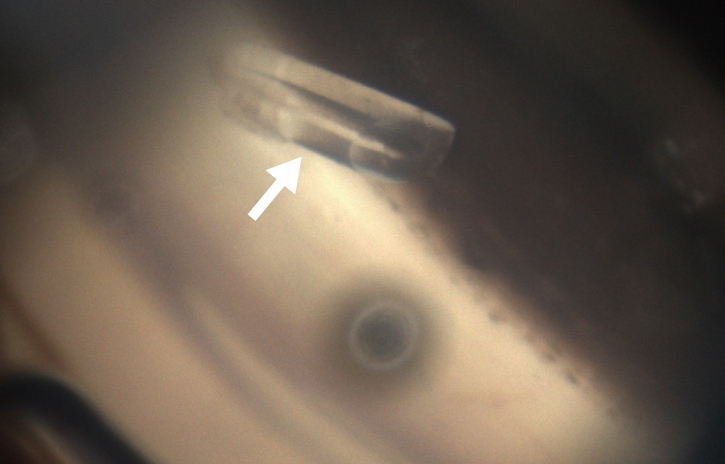
Conducto
Diagnóstico pre-operatorio: POAG (Glaucoma Primario de Ángulo Abierto, por sus siglas en inglés)
Punta visible de un dispositivo de drenaje del glaucoma
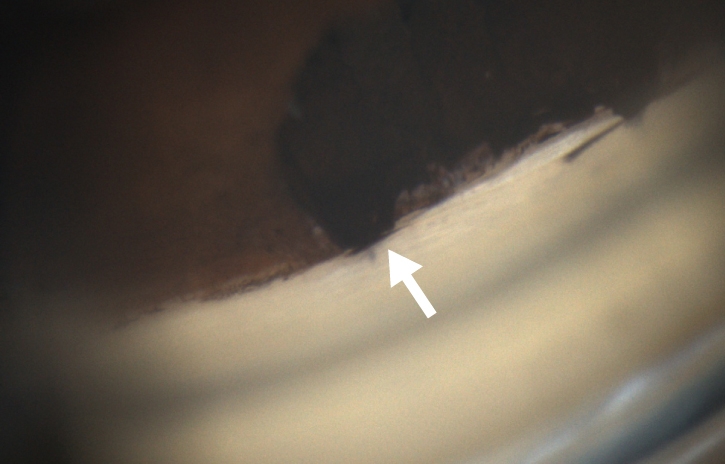

Trabeculectomía
Diagnóstico pre-operatorio: PACG (Glaucoma Primario de Ángulo Cerrado, por sus siglas en inglés)
Iridectomía quirúrgica delante de la escleroctomía con procesos ciliares visibles
Progresión de la Neovascularización (después de 5 meses) *
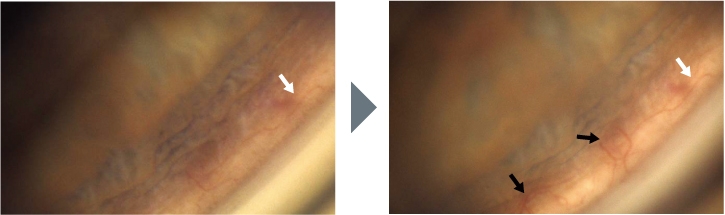
* Imagen cortesía del profesor C. E. TRAVERSO, MD, Clinica Oculistica, Di.N.O.G.M.I., Universidad de Génova – Ospedale Policlinico S. Martino, Italia
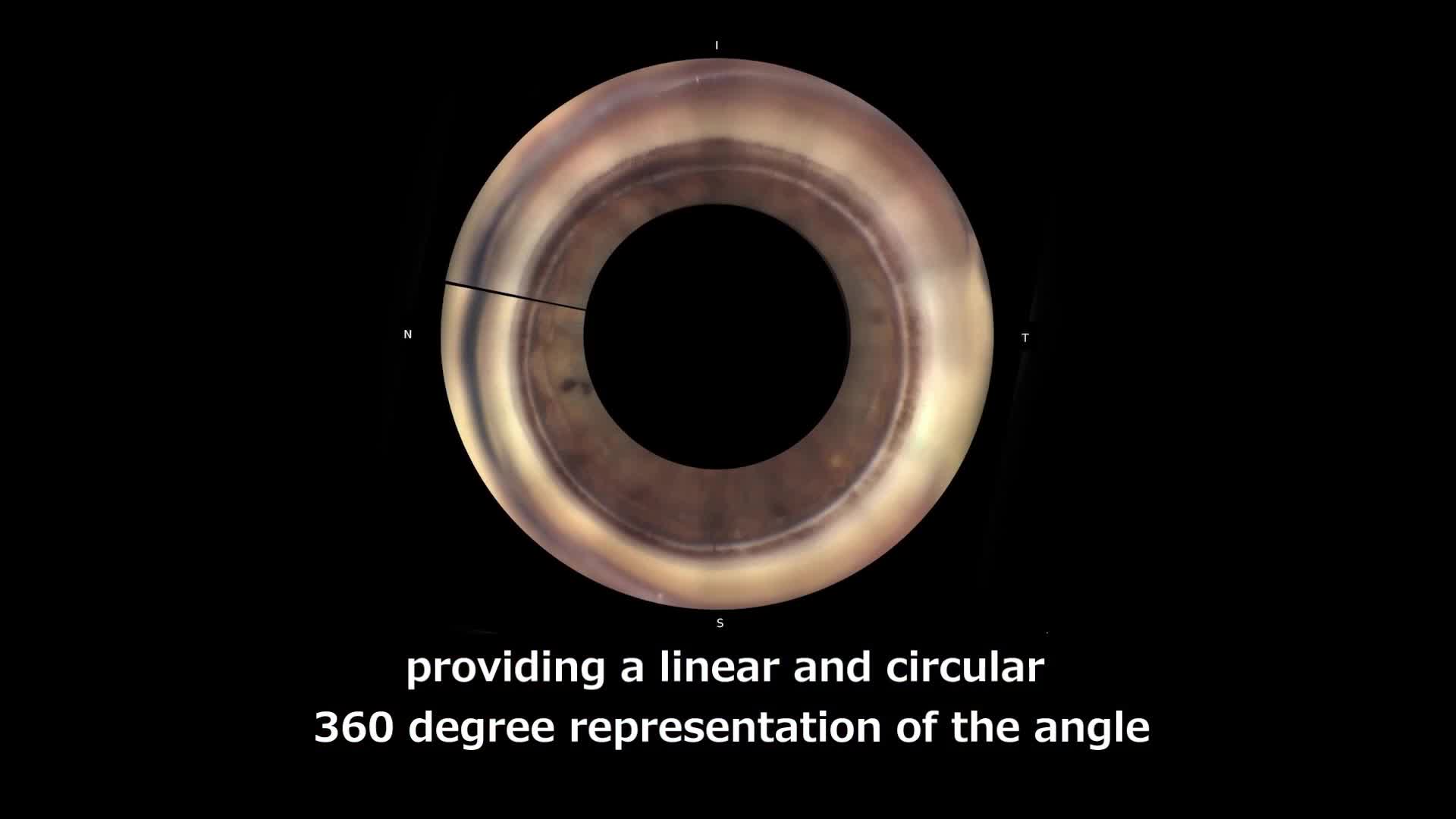
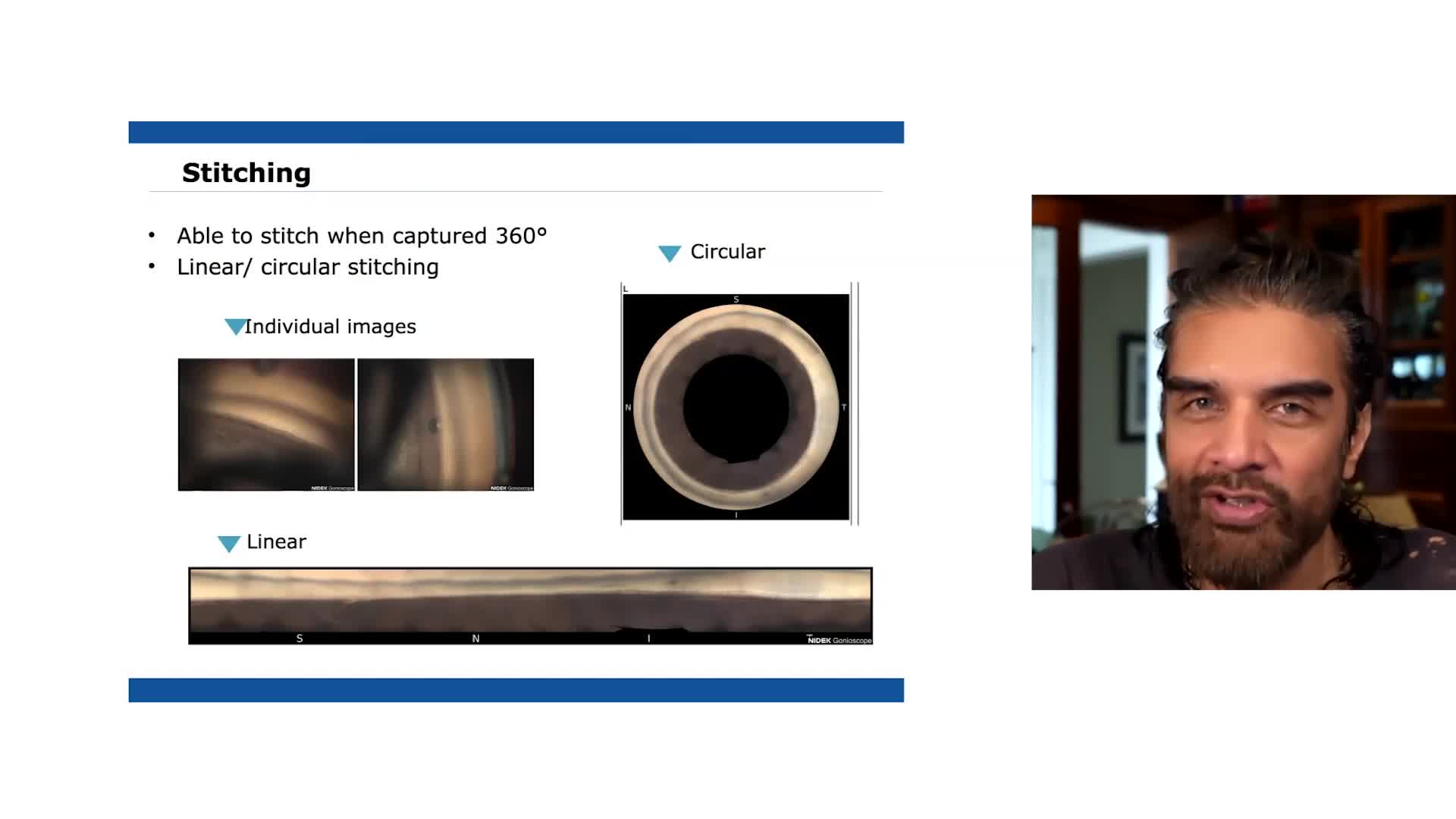
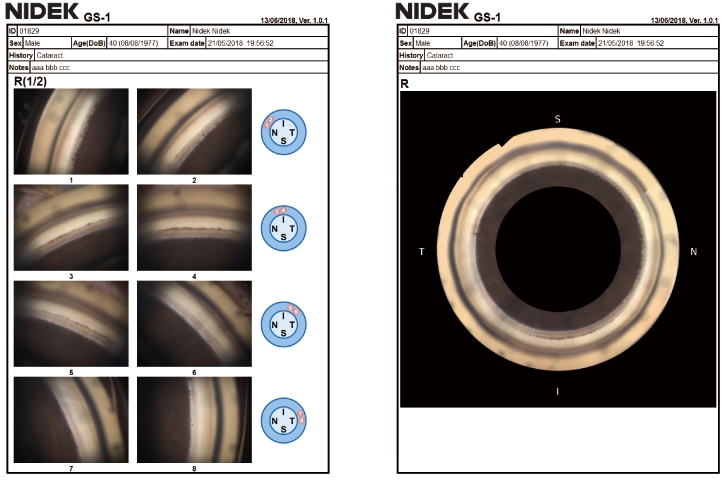
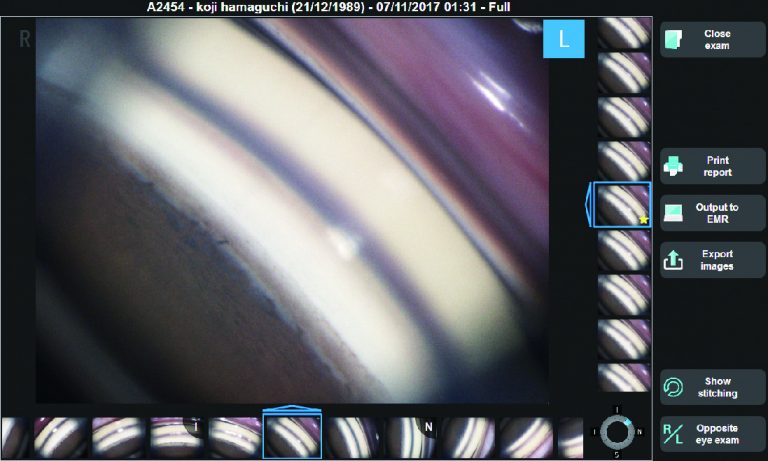
Gonofotografía circunferencial automatizada
Un sistema óptico interno gira automáticamente y adquiere fotografías en color del ángulo iridocorneal en 16 direcciones / 360 grados, documentando todo el ángulo. Cada dirección se puede capturar en 17 enfoques diferentes, lo que permite un enfoque versátil para la fotografía de ángulo iridocorneal.
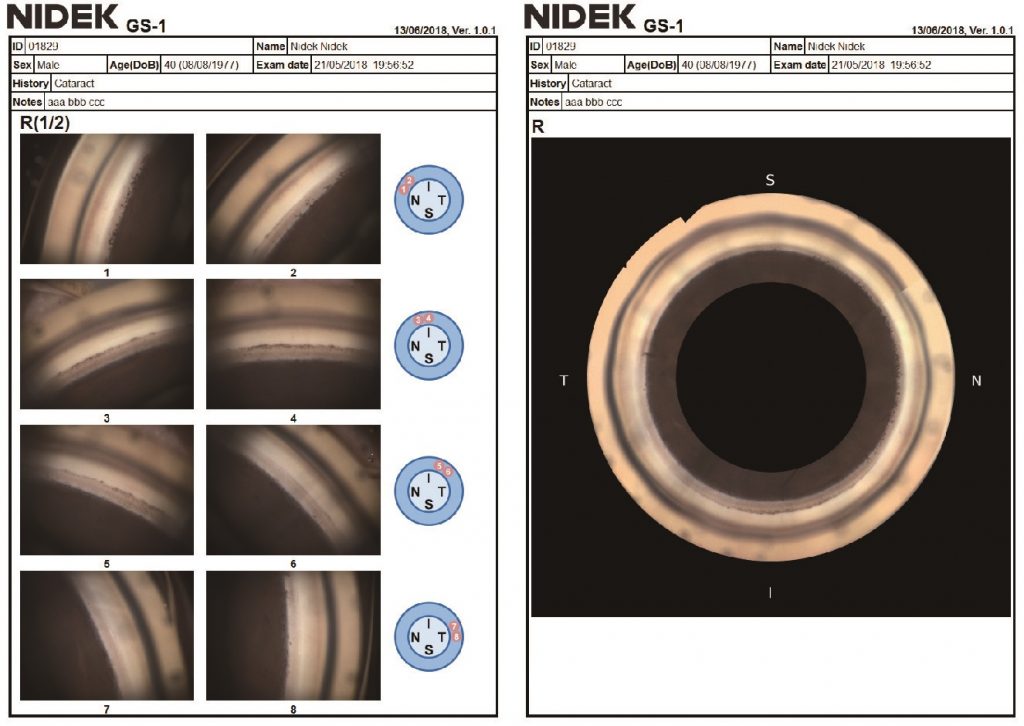
Exportando Imágenes
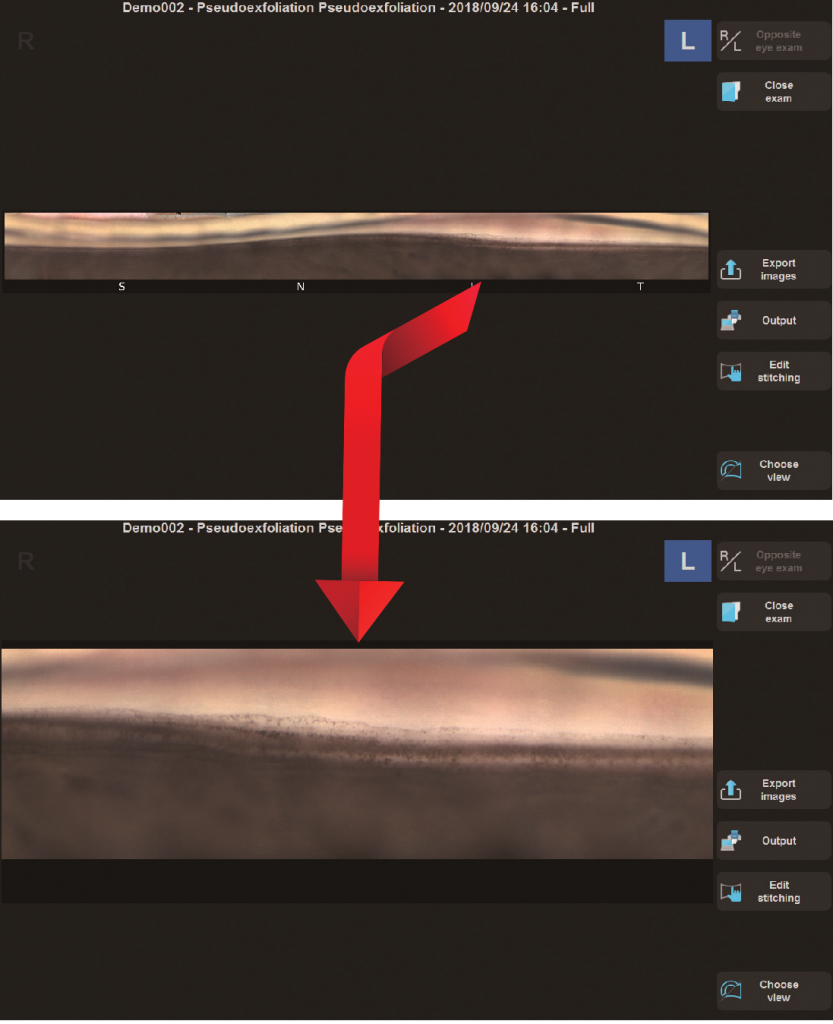
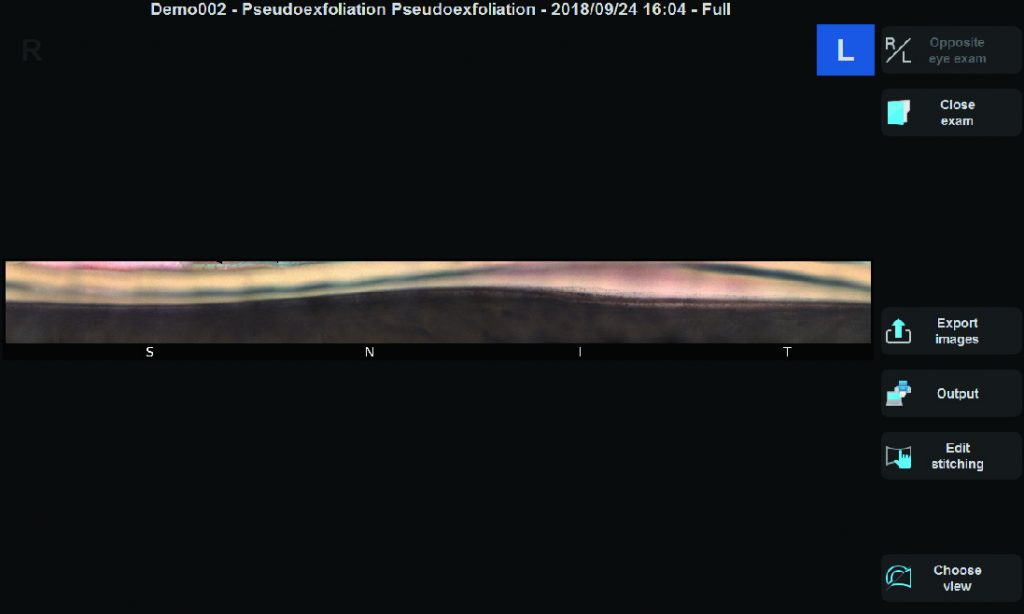
Las imágenes adquiridas por el GS-1 se pueden mostrar como una sola imagen, con costuras circulares o lineales. Además de la evaluación detallada con una sola imagen, la costura permite la ubicación de características / patologías en cualquier ángulo. Las imágenes en color de alta resolución se exportan en archivos JPEG, PNG y PDF.
Medición de Inmersión en Gel Sin Contacto
Para garantizar la comodidad del paciente, se utiliza un gel de acoplamiento durante la adquisición de imágenes. El prisma de espejo múltiple no está destinado a tocar la córnea.
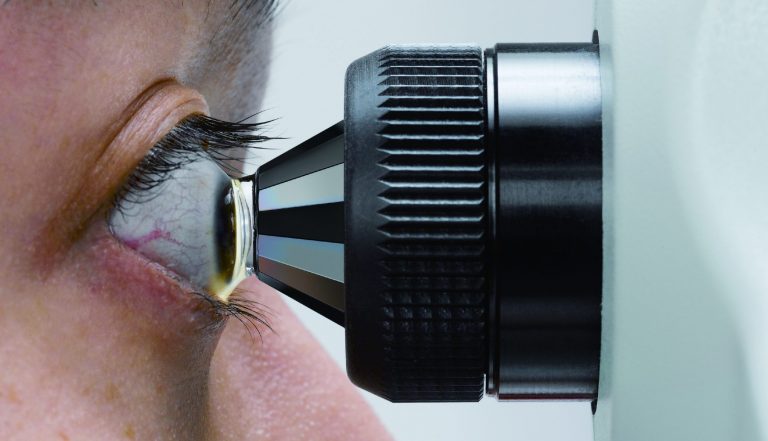

El GS-1 se puede utilizar como un dispositivo de diagnóstico así como para la formación clínica.
Las fotografías detalladas a color permiten compartir casos clínicos con compañeros de profesión.
También es útil para formar a aquellos médicos que tienen poca experiencia en la evaluación de la anatomía del ángulo iridocorneal.
El software GS Viewer permite visualizar y trabajar con datos del GS-1 a través del NAVIS-EX. Las funciones adicionales de este software amplían las capacidades del GS-1 y optimizan el flujo de trabajo clínico.
*NAVIS-EX es necesario para el GS Viewer y es opcional para el GS-1.
Nombre del producto/modelo: Software para relleno de imágenes NAVIS-EX
Gestión de datos

Con una gran capacidad de almacenamiento, la base de datos NAVIS-EX proporciona documentación de imágenes para evaluar la anatomía angular de visitas anteriores y de la última visita. La comodidad de recuperar imágenes retrospectivamente y compararlas con las imágenes de gonioscopia más recientes facilita la gestión del paciente y la evaluación del tratamiento a lo largo del tiempo.
Comparación de imágenes

Se pueden visualizar hasta dos imágenes unidas lineales/circulares o imágenes individuales para comparación, seguimiento y evaluación de cambios en la patología.
Enfoque total

Mediante el apilamiento de enfoque, se genera una imagen compuesta nítida a partir de hasta 15 imágenes con diferentes enfoques. La adquisición de imágenes puede ser realizada por personal sanitario auxiliar, lo que permite al médico evaluar las imágenes angulares.
Carlo E. Traverso, MD
Professor and Chairman, Clinica Oculistica University of Genova.
Policlinico Ospedale San Martino IRCCS, Italy
Traditional Goniophotography (e.g., manual photography of the angle) can be used for documenting and storing images of the angle structures.
However, it is technically challenging and time-consuming and hence, is not routinely performed in clinical practice. Documentation of the angle is clinically important for keeping preoperative and postoperative records in cases of lens extraction for angle closure, trabecular surgery, and trauma. Furthermore, this documentation may be particularly relevant if medicolegal issues arise. In my view, as an instrument capable of automated 360 degrees Goniophotography, the GS-1 is a significant addition for enhancing clinical workflow.
Fernando Gomez Goyeneche, MD
Emeritus Professor Hospital Militar Central, Colombia
«Gonioscopy findings could not only save your sight but your life.»
The availability of standardized digital image capture of the anterior chamber angle acquired by a technician represents a new chapter in the history of ophthalmology. Easy storage, retrieval and analysis of angle images taken over time have now become a clinical reality. On a more personal note, thanks to the NIDEK automated Gonioscope, we discovered a melanocytoma in my right eye that would have otherwise remained undetected. The GS-1 is an excellent screening tool for primary and surgical cases of glaucoma.
Luis Abegão Pinto, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor, Lisbon University, Portugal
Angle assessment is paramount in glaucoma management but remains a technically challenging procedure that is still performed manually by ophthalmologists. However, the recent introduction of the GS-1 automated gonioscopy device has allowed me to readily acquire high resolution 360º views of crucial angle structures, enhancing my ability to detect (and digitally store) clues for diagnosing pathology ranging from abnormal pigment to synechiae. The ability to magnify and analyze images allows greater familiarity with angle anatomy of each patient facilitating surgical planning.
This utility is particularly important in an era of increasing use of surgical implants for glaucoma. Additionally, the digital images acquired with the GS-1 are especially beneficial during rounds and for educating my residents (and my patients). Lastly, access to digital images of the angle allows me conveniently assess and plan SLT treatments. I perform SLT with the YC-200 S plus laser which houses an optical system that allows me visualize angle structures with the same clarity as my slit-lamp. This user friendly laser has excellent maneuverability that allows delivery of laser procedures even in challenging cases.
Alvaro Dantas, MD
ICONE- Instituto de Cirurgia Ocular do Nordeste (Northeast Eye Surgery Institute), Brazil
Automated gonioscopy with the NIDEK GS-1 has helped optimize my clinical routine. Capturing high quality images of the entire circumference of the trabecular meshwork and the ability to review the images at will has enhanced clinical management and treatment follow-up.
Most importantly, not taking manual notes on the gonioscopic exams allows me treat more patients and spend more time on care. The option to save images and generate reports allows me to thoroughly assess patient history (electronic documentation) and easily share the exam with other specialists for multidisciplinary consult. These advantages would not be possible without this device.
For MIGS surgeons, the GS-1 is an excellent tool for surgical planning, patient education and post-implant evaluation.
In summary, this one-of-a-kind device meets multiple clinical demands with the benefits of automated acquisition and documentation of gonioscopic images.
Carlo Alberto Cutolo, MD, PhD
Clinica Oculistica University of Genova.
Policlinico Ospedale San Martino IRCCS, Italy
The NIDEK GS-1 is a powerful device for collecting accurate true-colour pictures of the entire anterior chamber angle.
I currently use GS-1 primarily for three clinical applications:
– Document a closed-angle before performing an angle-opening procedure
– Document challenging cases necessitating close follow-up
– Record a view of the angle collected by a technician for asynchronous evaluations
Furthermore, having a dataset of good quality angle pictures comprising a broad spectrum of conditions is a potent tool for teaching gonioscopy to ophthalmologists-in-training, including increasing their familiarity of rare phenotypes. With the GS-1,
NIDEK has transformed the time-consuming and neglected task of manual gonio-photography into a friendly, easy and automated process. In my opinion the NIDEK GS-1 is not aimed to replace standard slit-lamp gonioscopy. Hence, the GS-1 should be considered a technique for improving anterior chamber angle assessments akin to wide-field retinography for ophthalmoscopy.